
s, -source addr Specify source address to use (doesn't affect -l) p, -source-port port Specify source port to use i, -idle-timeout Idle read/write timeout x, -hex-dump Dump session data as hex to a file

m, -max-conns Maximum simultaneous connections G Loose source routing hop pointer (4, 8, 12. g hop1 Loose source routing hop points (8 max) c, -sh-exec Executes the given command via /bin/sh U, -unixsock Use Unix domain sockets only 's' for seconds, 'm' for minutes, or 'h' for hours (e.g.
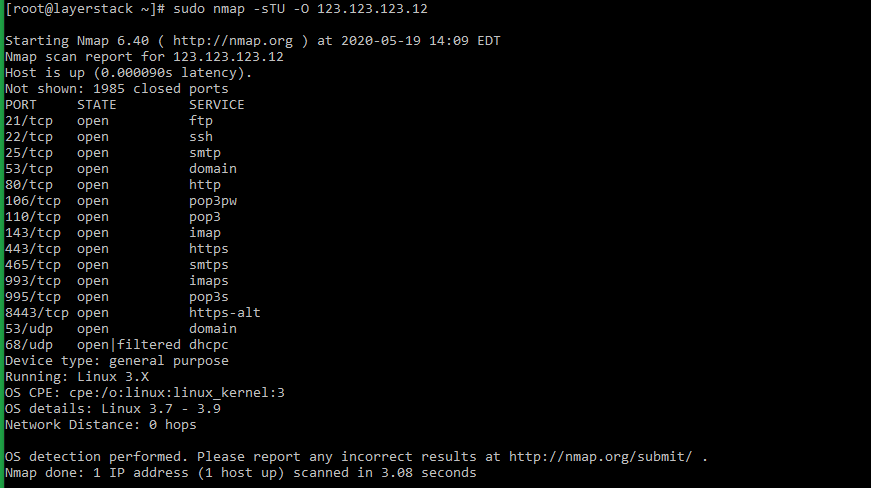
Ncat: Connection from 192.168.1.15:60393.Ĭoncatenate and redirect sockets :~# ncat -h Nping done: 1 IP address pinged in 4.13 secondsĬompare yesterday’s port scan ( yesterday.xml) with the scan from today ( today.xml): :~# ndiff yesterday.xml today.xml Using TCP mode ( –tcp) to probe port 22 ( -p 22) using the SYN flag ( –flags syn) with a TTL of 2 ( –ttl 2) on the remote host ( 192.168.1.1): :~# nping -tcp -p 22 -flags syn -ttl 2 192.168.1.1

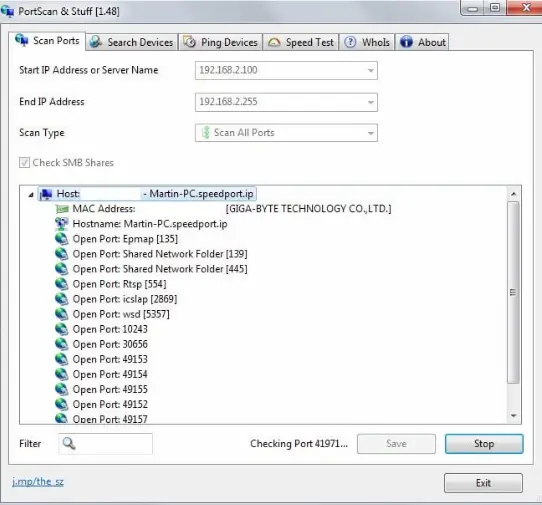
at 18:40Ĭompleted Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. Initiating Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. Scan in verbose mode ( -v), enable OS detection, version detection, script scanning, and traceroute ( -A), with version detection ( -sV) against the target IP ( 192.168.1.1): :~# nmap -v -A -sV 192.168.1.1Ĭompleted ARP Ping Scan at 18:40, 0.06s elapsed (1 total hosts) The router forwards correctly addressed packets to the sender service using the IP and port number.DARK Tool Documentation: nmap Usage Example The packet filter and firewall also ensure that packets that cannot be assigned to a local application are rejected. The public router IP, which also appears as the sender of data packets, is thus externally visible and addressable. Since unwanted network connections between local computers and the Internet are to be avoided as much as possible, the router IP usually comes between local IPs and destination addresses. The target application learns the sender port when the connection is established and sends the desired data packets back to the sender address. Open ports of target addresses “listen” for requests that originate via a port from private or public IPs. The destination address can be an app, a service, a website, or any other program such as a web browser. Transport protocols such as UDP (User Datagram Protocol) and TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) transfer data packets by assigning them to a specific address consisting of an IP and port number.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
